At first glance, the terms "digital signature" and "electronic signature" might seem similar. While both types of signatures are important, digital signatures and electronic signatures each have their own specific use cases.
In this article, we'll explore the differences between the two and help you determine which is right for your needs.
What is an electronic signature
An electronic signature is a signature in electronic form that is captured digitally and then added to a document.
In the United States, the federal Electronic Signatures in Global and National Commerce (ESIGN) Act defines an electronic signature or e-signature as "an electronic sound, symbol, or process attached to or logically associated with a contract or other record and executed or adopted by a person with the intent to sign the record."
An electronic signature serves the same purpose as a handwritten signature, identifying the person who signed the document. When you use an electronic signature, instead of pen and paper, you use your computer, smartphone, or other electronic devices to create your signature.
Electronic signatures provide a convenient way to sign documents without having to print them, physically sign them, and then scan or mail them back. It's a faster and more efficient way of getting things done online. E-signatures are commonly used to sign contracts, agreements, and other legal documents.
What is a digital signature

Digital signatures are more like electronic fingerprints that uniquely and securely associate a signer with a document in a recorded transaction.
Simply put, a digital signature is an advanced form of electronic signature that provides additional security and verification of the signer's identity through cryptographic techniques.
Digital signatures are mostly used for high-value financial transactions, sharing of confidential data, or other cases where it is important to detect forgery and tampering.
How digital signatures work
A digital signature provider employs a special protocol called the Public Key Infrastructure (PKI). This protocol uses a mathematical algorithm to secure your digitally signed document with two long codes, also called keys. The two types of keys are the public key and the private key.
To understand how digital signatures work with PKI, let's explore these foundational concepts.
Let's look at a use case:
John wants to sign and send a confidential document to Jane and ensure that it reaches Jane safely without any tampering in the process.
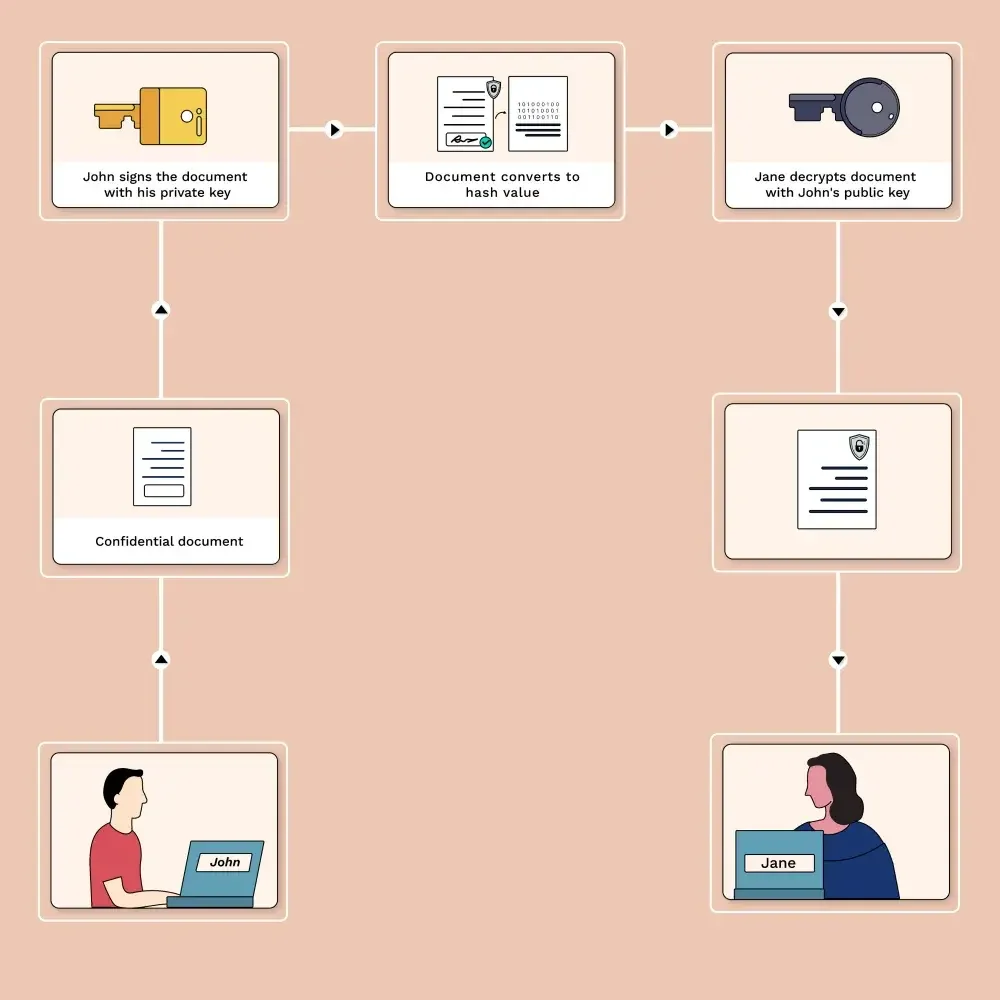
To digitally sign the document, John uses his private key. The private key converts the signed document into a unique set of zeros and ones called the hash value. The hash value bears the information about the document and the time it was digitally signed. John sends this to Jane along with his public key. The public key sent by John is the one corresponding to his private key, ensuring that the document that John encrypts with his private key can only be decrypted with his own public key.
If Jane is able to unlock the document from John using his public key, it proves two things to Jane.
- First, it authenticates the fact that it was signed by John: Nobody else has access to his private key, and only John's public key could help Jane do this unlocking.
- Second, it proves that no alteration or manipulation was done to the document midway, thus ensuring the integrity of the document. If it was altered by any means, the hash value of the document wouldn't be the same.
The role of certificate authority
A certificate authority (CA) builds a trusted framework that ensures digital signatures are valid and untampered.
A CA issues a digital certificate that contains the following information:
- Certificate's owner's name (John's name, in this case)
- Owner's public key and its expiration date
- The certificate issuer's name
- The certificate issuer's digital signature
So, John appoints a CA to help him generate the digital certificate information. The CA provides a digital certificate to John that he sends along with the signed document to Jane. Jane uses the public key given in the certificate to open the document sent by John. Now, Jane can be completely sure about the legitimacy and security of the document sent by John.
To summarize, a digital signature works to your advantage at three different levels.
- Authentication: A digital signature institutes trust that the document was created and sent by the claimer sender.
- Non-repudiation: With digital signatures, the sender cannot deny having sent the document later on.
- Integrity: A digital signature ensures that the document was not altered in transit.
Electronic signatures vs. digital signatures: Understanding the differences
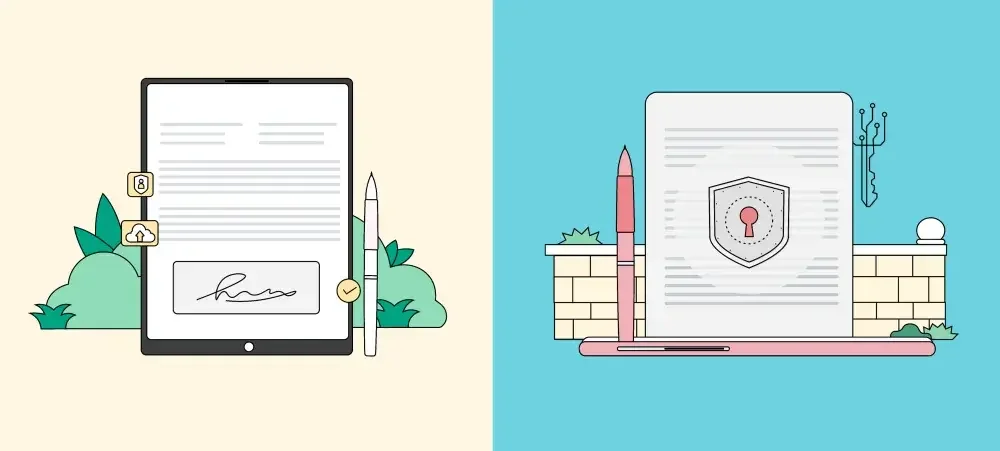

The core difference between an electronic signature and a digital signature is really one of degree: While an e-signature is used to simply execute a document, a digital signature is used to secure a document in its execution. In other words, a digital signature is really a special type of e-signature that uses advanced cryptographic encryption methods to provide additional security and verification of the signer's identity.
Some of their key differences can be summarized as follows:
1. Technology used
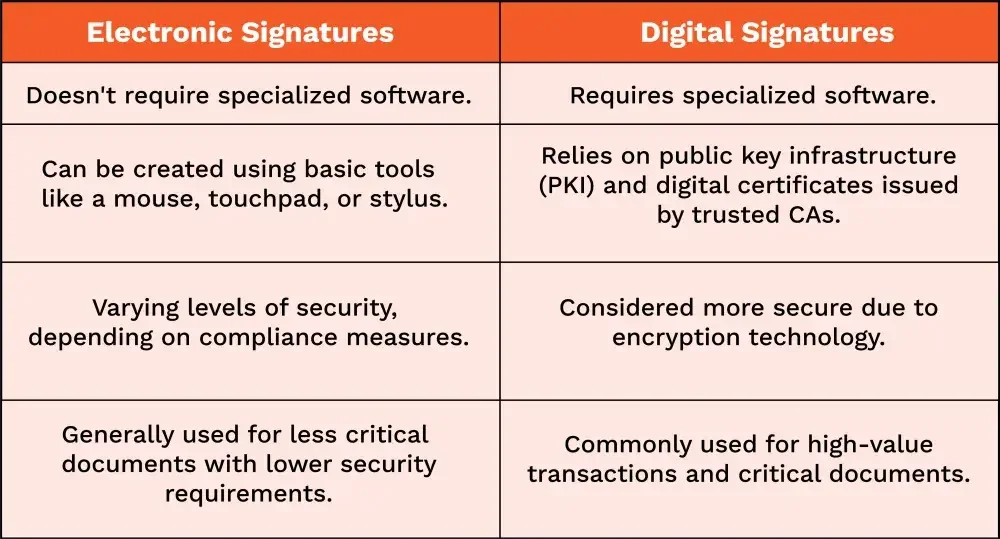
Digital signatures require specialized software, while electronic signatures can be created using basic tools such as a mouse, touchpad, or stylus. As mentioned earlier, Digital signatures rely on public key infrastructure (PKI) to authenticate the e-signature on a document.
2. Level of security
Digital signatures are generally considered more secure than electronic signatures because of the use of encryption technology. This means that any attempt to alter the document after it has been signed will result in an invalid signature.
While electronic signatures offer varying levels of security depending on the compliance measures followed, some electronic signature methods (like typed or scanned signatures) may be less secure than others and can be more vulnerable to fraud or forgery.
3. Usage criteria
Digital signatures are often used for high-value transactions, such as for signing government contracts, financial agreements, etc. By contrast, electronic signatures are generally used for less critical documents, such as offer letters, consent forms, and other documents that do not require a high level of security.
Here's a quick overview of the differences:
Understanding the legal acceptance of electronic and digital signatures
The legal validity of electronic signatures refers to how these types of signatures are recognized under the governing law. Differing jurisdictions around the world tend to treat electronic signatures differently. And since digital signatures, in particular, can vary based on the digital technology used by the provider and the steps involved, certain regions around the world have formed specific laws for different digital signature types.
For instance, under its eIDAS (Electronic Identification, Authentication, and Trust Services) Regulation, the European Union recognizes at least three forms of electronic signature technology, including advanced electronic signature (AES), qualified electronic signature (QES), and simple electronic signature (SES). However, these names are not commonly used outside the European Union. They are interpreted in the EU based on their signing process and laws under the eIDAS Regulation.
Here's what each e-signature means:
1. Simple electronic signature: A simple electronic signature is a basic form of electronic signature that can be a scanned image of a wet signature, a typed name, or a simple checkbox indicating agreement (clickwrap signature). It provides a basic level of authentication and is commonly used for informal or low-risk transactions.
2. Advanced electronic signature: An advanced electronic signature is more secure than an SES. This type of signature uses cryptographic techniques to verify the identity of the signer and ensure the integrity of the signed document. This is used for high-risk documents that require a higher level of security.
3. Qualified electronic signature: It is the most secure electronic signature that is created using a qualified certificate issued by a trusted certification authority. They also require an electronic signature creation device, such as a smart card or USB token. Both AES and QES use techniques similar to how a digital signature is created.
The European Union is not the only place that recognizes QES. In fact, Thailand, which uses a two-tier eSignature law, permits qualified electronic signatures under the Electronic Transactions Act of 2001.
In the United States, the Electronic Signatures in Global and National Commerce (ESIGN) Act and the various Uniform Electronic Transactions Acts (UETA) validate electronic signatures at the federal and state levels, respectively. These laws establish that electronic signatures carry the same legal weight and enforceability as their handwritten counterparts, as long as certain requirements are met.
Canada's Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act (PIPEDA) addresses the legal validity of electronic signatures at the federal level. PIPEDA defines an e-signature as “a signature that consists of one or more letters, characters, numbers or other symbols in digital form incorporated in, attached to or associated with an electronic document."
In conclusion, the legal acceptance of electronic and digital signatures varies across jurisdictions, with different regions having specific laws and regulations governing their use. It is essential to understand and comply with the legal frameworks surrounding them in order to ensure their validity and enforceability in electronic transactions.
It is best to consult an attorney if you have any questions about the acceptance of electronic signatures in your jurisdiction.
Advantages of electronic signatures over digital signatures

While both electronic signatures and digital signatures have their place, there are a few advantages that electronic signatures have over digital signatures:
Accessibility
Electronic signatures can be created using basic tools such as a mouse, touchpad, or stylus, making them more accessible and user-friendly compared to the specialized software and hardware required for digital signatures.
Ease of use
Electronic signatures are typically easier to implement and use, as they do not require complex encryption technology or the management of PKI that digital signatures rely on.
Cost-effectiveness
Implementing electronic signatures is often more cost-effective than setting up and maintaining the infrastructure required for digital signatures, which can involve significant expenses related to software licenses, hardware devices, appointing a third-party trusted CA for providing digital certificates, etc.
User experience
With electronic signatures, signers can electronically sign documents using any smart device like a computer, or smartphone, providing a seamless signing experience compared to digital signatures.
Adopt LegalZoom's electronic signature service to e-sign your documents faster
When it comes to selecting the right signature method for your everyday business needs, both digital signatures and electronic signatures offer distinct advantages. However, for situations where the additional security provided by digital signatures is not necessary, LegalZoom's eSignature service emerges as the ideal choice.
Our eSignature service simplifies the process of creating and signing documents electronically, eliminating the need for tiresome manual paperwork. The service uses encryption technology to keep your data safe, and it complies with state and federal electronic records and signature laws..
Whether you operate a small business, work as a freelancer, or represent a large corporation, LegalZoom's eSignature service offers the flexibility and security you need for efficient document signing.
FAQs
What is the difference between digital signatures and electronic signatures?
An electronic signature is a way of signing a document using electronic means. It can be an electronic symbol, sound, text, or sign that indicates a signer's agreement to the terms of a document. A digital signature is a special type of electronic signature that is created using a digital certificate and cryptographically attached to the document using public key infrastructure (PKI).
When should you use electronic signatures and digital signatures?
Electronic signatures and digital signatures have specific use cases. Here are some guidelines to help you decide.
Use electronic signatures when:
- You need a simple and convenient way to sign documents electronically.
- You don't require a high level of security or compliance.
- You have to sign your HR documents, invoice receipts, rental agreements, etc.
Use digital signatures when:
- You need a high level of security and integrity for your documents.
- You need to comply with specific legal requirements or regulations.
- You are working in industries where security and compliance are critical, such as finance, healthcare, or government.
Is an electronic signature a digital signature?
No, an electronic signature is not the same thing as a digital signature. An electronic signature is a way to sign a document using an electronic method, such as typing your name, drawing your signature with a mouse or stylus, or using an e-signature service. On the other hand, a digital signature is a type of electronic signature that uses cryptographic algorithms to bind a digital signature to a specific document. This process creates a unique fingerprint of the document and ensures that any tampering with the document can be detected.
What is the difference between an electronic signature and a digital certificate?
An electronic signature is a method of signing an electronic document. On the other hand, a digital certificate is a digital document that helps in the creation of digital signatures. To generate credible digital signatures, digital certificates must be obtained from trusted certification authorities (or CAs).

