Intellectual property (IP) refers to protectable original creations and includes copyrights, patents, trademarks, and trade secrets. IP other than patents is sometimes called soft IP.

In this article, we'll dive into the specifics of soft IP and cover everything you need to know, including how it compares to hard IP, its importance to content creation, and soft IP valuation.
Overview: What is soft IP?
Soft IP is intellectual property other than patents, including copyrights, trademarks, and trade secrets. It can also describe other assets that are harder to categorize, such as general knowledge about a product or confidential information held by a company.
The distinction may have arisen because patents often apply to tangible items, such as machinery, products, and other physical inventions.
Soft intellectual property is not a generally accepted legal term, although it is sometimes used in contracts or agreements.
For example, a contract selling a company's intellectual property rights might include "soft property." But it's best to use specific legal terminology about the items that are being managed or sold for clarity. The contract might mention that items in the sale include copyrights, patents, trademarks, and trade secrets. Using the exact, correct terminology for the intellectual property in question makes it easier to manage and may also make it easier to sell, should you ever wish to.
Types of IP
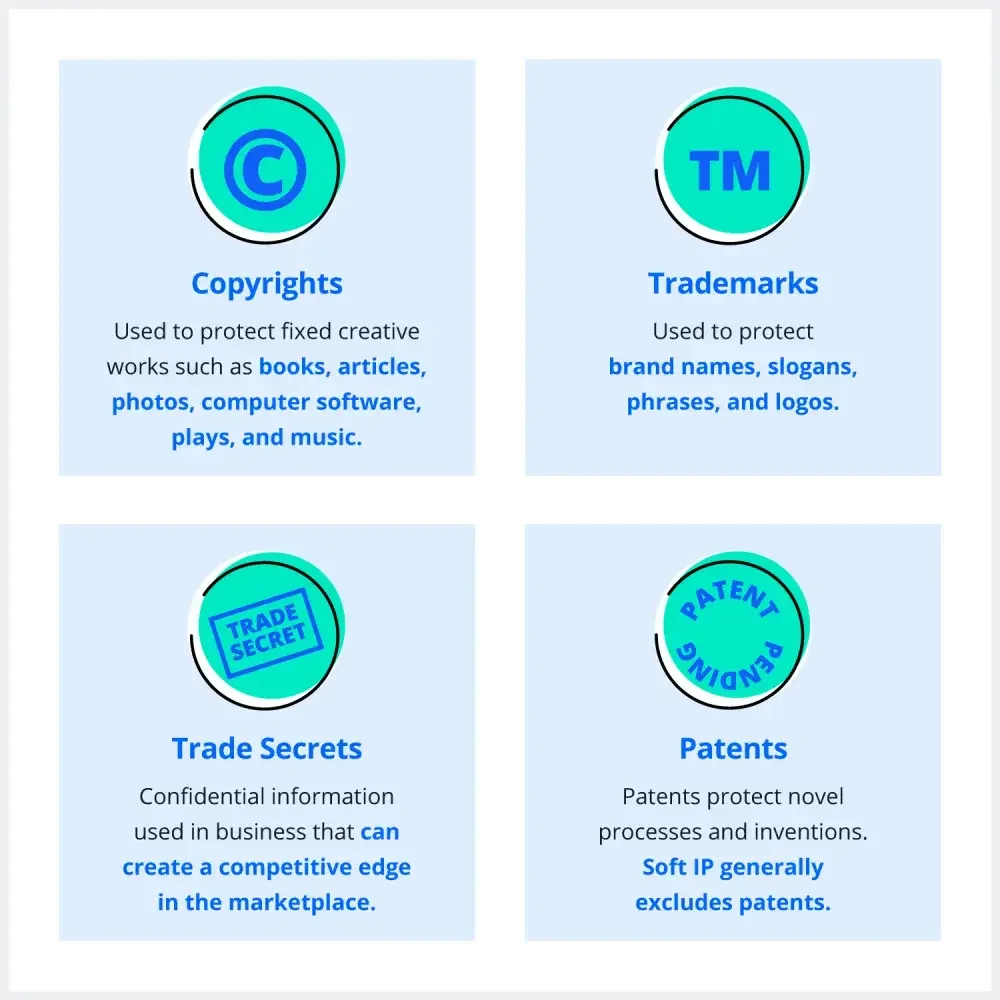
There are four types of intellectual property that protect different types of work. Soft IP typically refers to nontangible items that are protected by copyrights, trademarks, and trade secrets.
Soft IP vs. hard IP: What's the difference?

The main distinction between the two intellectual properties is that soft IP excludes patents. Patents often cover physical items or inventions, while copyrights, trademarks, and other IPs may cover more intangible property.
Soft IP management
Because soft intellectual property can be a key part of a business's value, it's important to manage it carefully. Large companies have entire departments devoted to intellectual property management.
If you own a small business, you may be able to manage it yourself but should consider obtaining legal help. You can do this by identifying all intellectual property that your company owns and determining which type it is.
Be sure to register trademarks and copyrights owned by your business and protect confidential information with nondisclosure agreements and noncompete clauses.
Soft IP and content creation
Soft intellectual property rights can be crucial for protection, especially when there's a risk of a content creator's hard work getting stolen and copied.
Importance of soft IP rights
Understanding soft IP rights are important for all sorts of content creators. As a content creator, you have the power to decide on the reproduction and distribution of your work when you have intellectual property rights. Soft IP rights are also important to have in a legal sense, as they allow you to sue for damages if and when your creation is misused by others.
Check out some more reasons why soft IP is important for content creators:
- Soft IP protects your company's marketing and branding strategies from misuse and imitation.
- Soft IP helps distinguish your creations from competitors'.
- It allows you to protect your work from those who create counterfeits.
How content creators can protect their IP
As a content creator, protecting your intellectual property is a way to secure an economic advantage for your business and make sure you can defend your unique ideas. The best way to protect soft IP from copyright issues is to register it with the government and enforce your ownership rights.
Beyond registration and enforcement, content creators can protect certain types of soft intellectual property by:
- Using digital rights management
- Opting for strong nondisclosure agreements
- Creating strong access credentials
How to value soft intellectual property
Soft intellectual property has value, and that value can be important for your business. Because it's part of your company's total worth, it can affect your ability to obtain loans and impact your business's total valuation when it is sold.
There are three approaches that can be used to calculate the value of soft intellectual property: market, cost, and income.
Market approach
If there is a current market for the type of property, you can look at comparable sales to determine its value. For example, if you have a nonfiction book about computer programming, you would check similar books to see how much they sell for and how many copies they have sold.
Cost approach
You can calculate the value based on the cost of creating or replacing the item. If you are valuing a trademark, you would examine all the costs that went into creating the brand, including filing expenses, to determine a valuation.
Income approach
Using this method, the income generated from the intellectual property asset is evaluated to calculate a value. If you are appraising computer software, you will project the income expected from selling it.
It is important that your business protect all of its intellectual property, soft or otherwise. Doing so will help increase your company's value, so be sure that you have a system in place to manage every aspect of your intellectual property.
Learn how to defend expressions of your ideas against theft by registering your intellectual property and speaking with an intellectual property attorney who can help ensure that the best possible protection is secured for your work.

